| ||||
Mode of Action of
Penicillin Antibiotics
There are many different classes of antibiotics
each exerting a different type of inhibitory effect that specifically impacts bacteria. Bacterial cells are prokaryotic; primitive cells that differ significantly from humans’
Article Summary: Antibiotics are chemotherapeutic agents used to inhibit or kill bacteria. But how do penicillins (a type of beta-lactam) destroy these microbes without hurting our cells?
MOA of Penicillin (Beta-lactam) Antibiotics
Page last updated: 4/2016
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
Beta-lactams exert their bactericidal effect by inhibiting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall.
Each article in this series covers a specific class of antibiotic and includes the following information:
- list of the specific antibiotics that fall in the class (generic and brand names)
- mode of action (how it works)
- type of infections the antibiotic class is used against
- type of bacteria inhibited or killed
- pros and cons of using the class of antibiotics
Main Classes of Antibiotics
(a Beta-lactam)
- Penicillins (a Beta-lactam)
(Fluoroquinolones)
(Sulfa Drugs)
Penicillin Antibiotics
In 1929 Alexander Fleming, a British biologist, inadvertently discovered penicillin. He had observed bacterial
Staphylococci colonies disappearing in cultures that were contaminated with mold.
Fleming eventually extracted the compound from the mold that had been responsible for destruction of the bacterial colonies. The product was named penicillin, after the Penicillium mold from which it was derived.
Some examples of penicillins include:
- amoxicillin
- ampicillin
- bacampicillin
- oxacillin
- penicillin
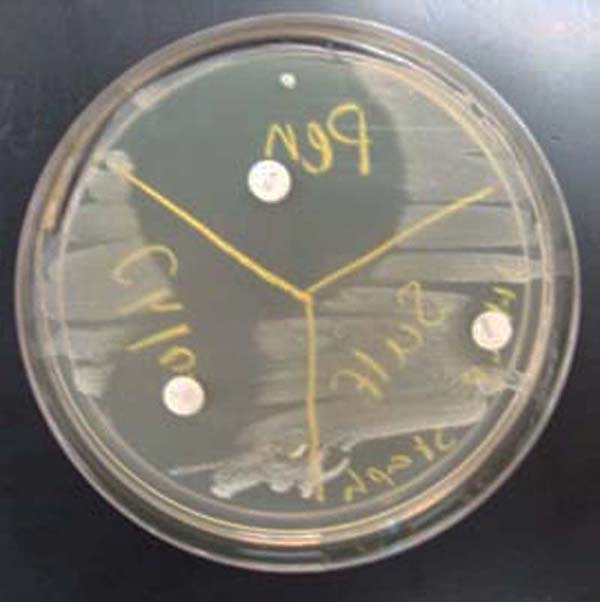
Above: TSY agar inoculated with Staphylococcus,
a Gram-positive bacterium.
Three antibiotic sensitivity disks appear on this plate: penicillin, sulfa, and ciprofloxacin (clockwise from top).
Note the "zone of inhibition" around each antibiotic disk. The larger the zone of bacterial inhibition, the more effective the antibiotic is against the bacteria.
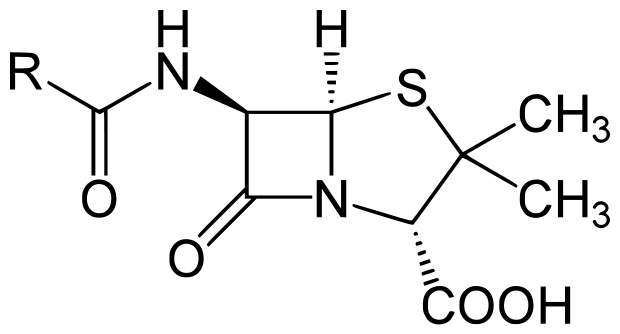
Penicillin core structure, where "R" is the variable group.
Continued ...
Infections Penicillins Are Used Against
Penicillins are used to treat Gram+ bacterial infections which, depending on the specific microbe involved, cause a wide range of illnesses including skin infections, dental infections, ear infections, respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, and gonorrhea.
Mode of Action
Penicillins, and other beta-lactam antibiotics, work by interfering with interpeptide linking of peptidoglycan, the a strong, structural molecule found specifically bacterial cell walls. Cell walls without intact peptidoglycan cross-links are structurally weak, prone to collapse and disintegrate when the bacteria attempts to divide. Since the eukaryotic cells of humans do not have cell walls, our cells are not damaged by penicillins.
Antimicrobial Spectrum of Penicillins
Penicillins have a bacteriocidal effect on Gram-positive bacteria. In Gram-positive cells, peptidoglycan makes up as much as 90% of the thick, compact cell wall, and is the outermost layer.
Penicillins are not effective against Gram-negative bacteria, which have cell walls in which peptidoglycan is not the outermost layer, but that lies between the plasma membrane and a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) outer membrane. Penicillin cannot access the peptidoglycan of Gram-negative cells.
Alexander Fleming (1881 – 1955), the Scottish biologist & pharmacologist credited for discovering penicillin.
 | ||||||
HOME MICROBIOLOGY EXPERIMENT FROM SPO
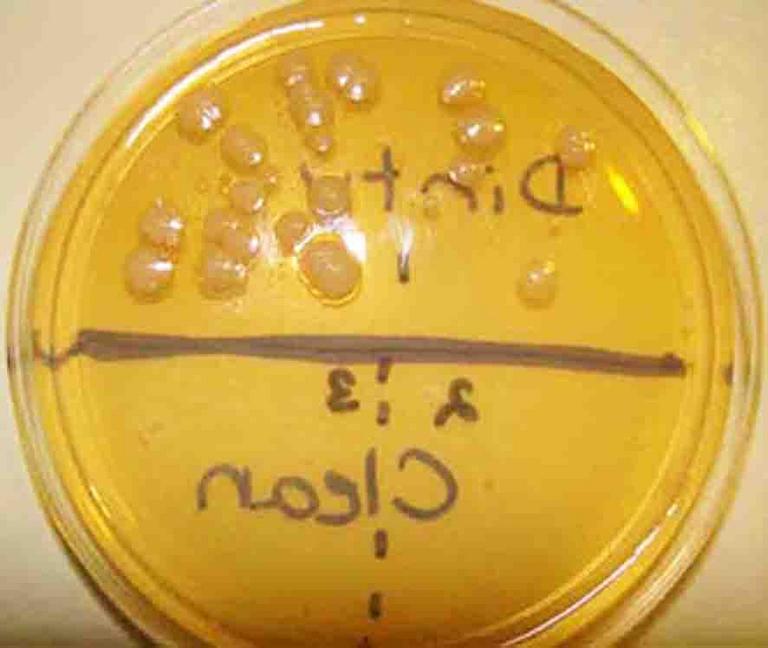
TSY agar with sample from dirty dishes on top (note bacterial colonies that grew), and sample from cleaned dishes on bottom.
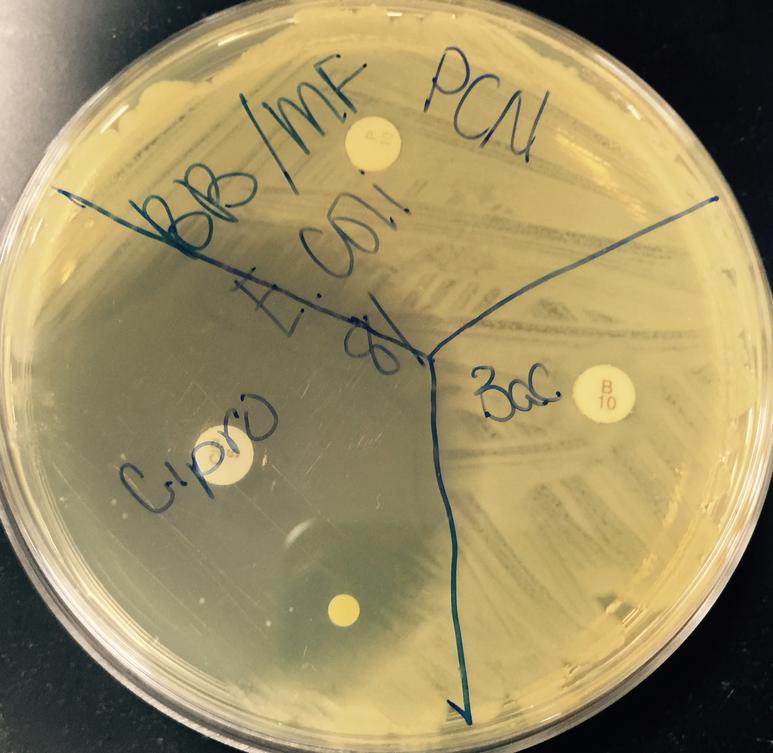
Above: TSY agar inoculated with Escherichia coli,
a Gram-negative bacterium.
Three antibiotic sensitivity disks appear on this plate: penicillin, bacitracin and ciprofloxacin (clockwise from top).
Note the "zone of inhibition" only around the cipro. The larger the zone of bacterial inhibition, the more effective the antibiotic is against the bacteria.
This plate demonstrates that penicillin and bacitracin are not effective against Gram-negative bacteria.
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in two college-level introductory microbiology courses (8-week & 16-week). The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.