| ||||
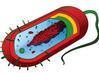
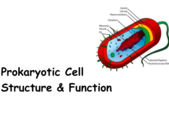
Prokaryotic Cell
Parts, Functions & Diagrams of Prokaryotes
Single-celled prokaryotes are microbes that include bacteria and their bacteria-like cousins Archaea. Prokaryotic cells are much simpler than the more evolutionarily advanced
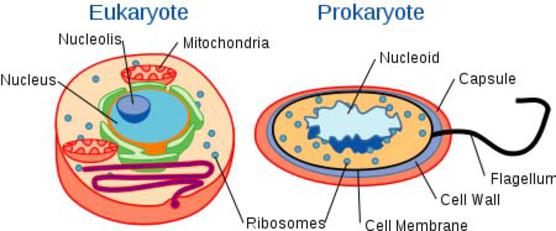
Whereas eukaryotic cells have many different functional compartments, divided by membranes, prokaryotes only have one membrane (the plasma membrane) enclosing all of the cell’s internal contents.
If a eukaryotic cell is analogous to a big house with many different rooms, a prokaryotic cell is like a one-room, studio apartment.
Article Summary: Prokaryotes are simple, single-celled, yet remarkably successful organisms. Here's an overview of the structures and functions of prokaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic Cell Structures, Functions & Diagrams
You have free access to materials used in two college-level introductory microbiology courses (8-week & 15-week).
The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
 | ||||||
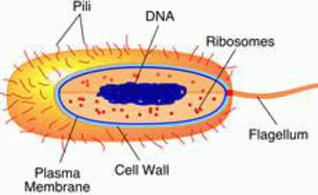
Internal Structures of Prokaryotic Cells
- Cytoplasm: This is the gel-like fluid that the cell is filled with, inside the plasma membrane; liquid with all of the cellular organelles suspended within.
Page last updated: 10/2016
- Cytoskeleton: It's only recently been discovered that rod-shaped bacteria and Archaea possess cytoskeletal proteins that function in a similar way to the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells. This scaffolding provides structural support to the cell and plays a role in cell division.
- Ribosomes: All cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, have multiple ribosomes within. Ribosomes are the tiny protein-making machines that carry out the genetic instructions of the cell.
 | ||||||