| ||||
Prokaryotic Cell Structures, Functions & Diagrams - P3
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
Sources & More Helpful Links on Biological Cells
- Bauman, R. (2014) Microbiology with Diseases by Taxonomy 4th ed., Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
- Becker, W. M. et. al. (2009) The World of the Cell. Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
- Inside a Cell, interactive cell diagram from University of Utah.
- Eukaryotic Cell Tour interactive exercise.
- Tour of a Cell Video by Paul Anderson.
- Eukaryotic Organelles Animation from Sumanis.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum & Golgi Bodies from Khan Academy.
- Cell Structure Interactive Animation from Wiley.com.
- Eukaryotic Cell Structure & Function Lecture Main Page, Virtual Cell Biology Classroom.
PAGE 3 < Back to Page 2
Genetic Material of Prokaryotes
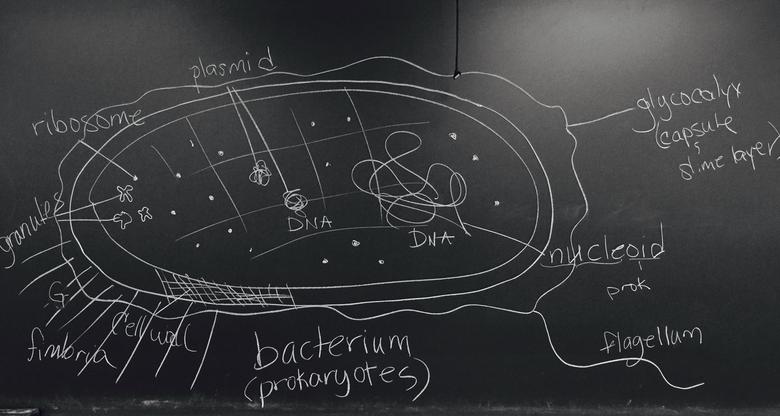
- Nucleoid: The nucleoid is the region of the prokaryotic cytoplasm that contains the genome—the main genetic material (DNA) of the cell. Bacteria and Archaeans typically have a single, circular chromosome.
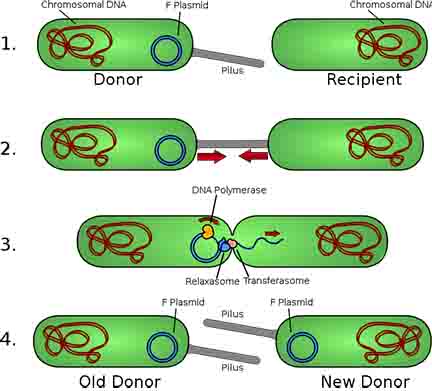
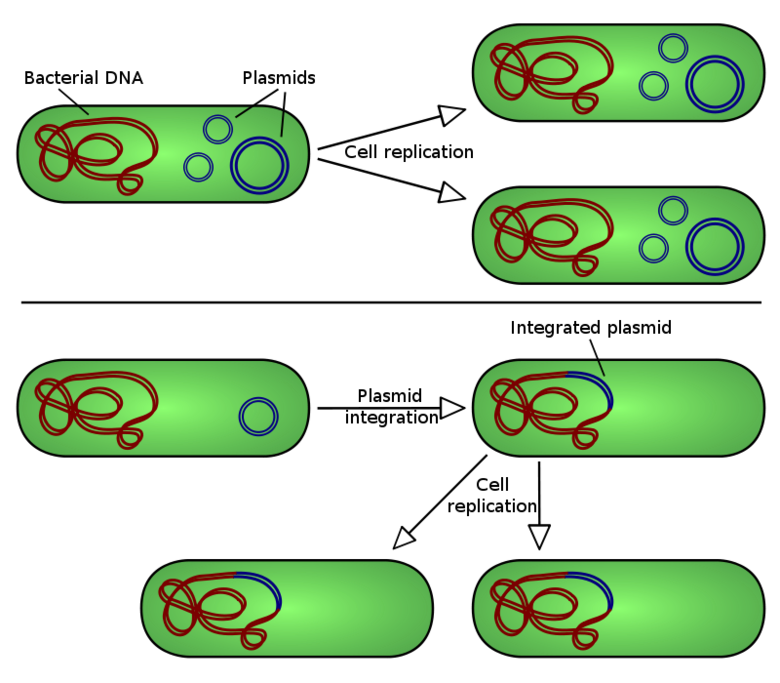
- Plasmids: In addition to the nucleoid (bacterial chromosome), bacteria may also contain one or more plasmids. A plasmid is a non-essential piece of DNA that confers an advantage to the bacteria, such as antibiotic resistance, virulence (the ability to cause disease) and conjugation (a bacterium’s ability to share its plasmids with other bacteria). Plasmids are also found in some eukaryotic microbes, such as yeasts.
Conjugation is a type of horizontal gene transfer that bacteria use to share plasmids with each other.
FREE Educational Materials on Prokaryotic Cells
- Prokaryotic Cell Structure & Function Lecture Main Page from the VCBC.
- Meet the Prokaryotes Lecture Main Page from the VMC.
The Virtual Cell Biology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including Power Point Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
Page last updated: 10/2016
Plasmid Replication