| ||||
Mode of Action of Macrolide Antibiotics
Class Notes from Science Prof Online
There are many different classes of antibiotics
each exerting a different type of inhibitory effect that specifically impacts bacteria. Bacterial cells are prokaryotic; primitive cells that differ significantly from humans’ eukaryotic cells.
Macrolides exert their bacteriocidal effect by interfering with protein
synthesis (translation) in bacterial cells.
Article Summary: Antibiotics are chemotherapeutic agents used to inhibit or kill bacteria. But how do macrolides destroy these microbes without hurting our cells?
MOA of Macrolide Antibiotics
 | ||||
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in a college-level introductory microbiology course. The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
Page last updated: 5/2014
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
 | ||||||
SPO is a FREE science education website. Donations are key in helping us provide this resource with fewer ads.
Please help!
(This donation link uses PayPal on a secure connection.)
This article is part of an antibiotic MOA serites. Each article in this series covers a specific class of antibiotic and includes the following information:
 | ||||||
HOME MICROBIOLOGY EXPERIMENT FROM SPO
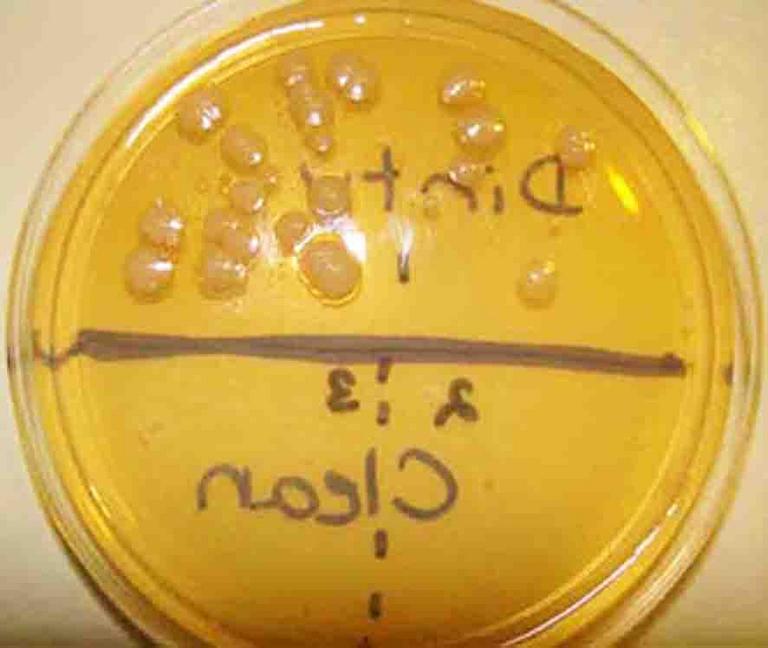
TSY agar with sample from dirty dishes on top (note bacterial colonies that grew), and sample from cleaned dishes on bottom.
Sources & Resources
- Bauman, R. (2014) Microbiology with Diseases by Taxonomy. Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
- Park Talaro, K (2008) Foundations in Microbiology, McGraw Hill.
- Bayarski, Yuri, "Antibiotics and Their Types, Uses and Side Effects".
- Microbiology In the Home: Tips To Sanitize Your House and Keep Your Family Healthy, Household Microbiology article from Science Prof Online.
- Microbial Control Laboratory Exercise Main Page from the Virtual Microbiology Classroom.
- a list of the specific antibiotics that fall in the class (generic and brand names)
- mode of action
- type of infection the antibiotic class to against
- type of bacteria inhibited or killed
- pros and cons of using the class of antibiotics
Main Classes of Antibiotics
- Cephalosporins (a Beta-lactams)
- Macrolides
- Penicillin (a Beta-lactam)
- Quinolones (Fluoroquinolones)
- Sulfonamides (Sulfa Drugs)
Macrolide Antibiotics
Erythromycin, and closely related antibiotics, are called macrolides. They include the following commonly prescribed antibiotics:
- azithromycin (Zithromax®, Zitromax®, Sumamed®)
- clarithromycin (Biaxin®)
- dirithromycin (Dynabac®)
- erythromycin
- roxithromycin (Rulid®, Surlid®, Roxid®)
Some of the more recent additions the macrolide group are azithromycin and clarithromycin. They work the same way as the other macrolides, but are typically more effective with fewer side effects.
Mode of Action
Macrolides exert their antibiotic effect by binding irreversibly to the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes. Ribosomes are the protein factories of the cell, and by binding to the ribosome, macrolides inhibit translocation of tRNA during
translation (the production of proteins under the direction of DNA). Although the cells of humans also have ribosomes, these eukaryotic cellular protein factories differ in size and structure from the ribosomes of prokaryotes.
This action is mainly bacteriostatic, meaning that bacterial growth and reproduction are inhibited, in contrast to bactericidal antibiotics which directly kill bacteria. Macrolides can be bactericidal in high concentrations.
Type of Infections Macrolides Are Used Against
Macrolide antibiotics are used to treat infections of the respiratory tract, genital, gastrointestinal tract, and soft tissue infections caused by strains of bacteria susceptible to this class of antibiotics.
Antimicrobial Spectrum of Macrolides
Like penicillin, these drugs are effective against beta-hemolytic Streptococci, pneumococci, Staphylococci and Enterococci. Macrolides are, however, effective against a slightly wider range of bacteria than is penicillin, including Mycoplasma, Mycobacteria, some rickettsia and chlamydia.
Adverse Effects of Macrolides
Macrolides are less likely to cause allergy problems than are the penicillins and cephalosporins, and are commonly used in patients with an allergy to penicillin. Macrolide antibiotics can cause irritation to the stomach.
* The information in this article is not meant to be used for self-diagnosis or treatment of illness. If you are sick, seek help from a trained medical professional, not a computer.
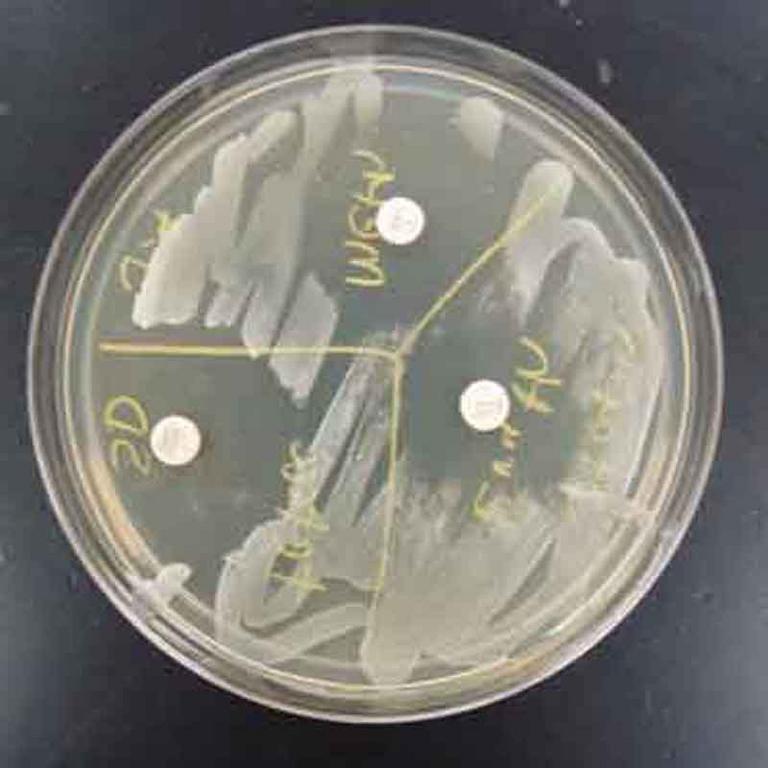
TSY agar inoculated with Staphylococcus. Three antibiotic sensitivity disks appear on this medium: bacitracin, erythromycin, and tetracycline (clockwise from top). Note the "zone of inhibition" around each antibiotic disk. The larger the zone of bacterial inhibition, the more effective the antibiotic is against the bacteria.
Erythromycin: The macrolide ring is the lactone (cyclic ester) at upper-left.