| ||||
What Are Normal Flora?
Resident, Transient and Opportunistic Microbes
Within the womb, a baby’s body is axenic, meaning that the environment within the uterus is sterile. During and after birth, the newborn becomes colonized by microbes, most of which are beneficial to human health. These bacteria are called normal flora or normal microbiota.
Article Summary: The human body is made up of about 10 trillion cells, but hosts 100 trillion more. The vast majority of cells living on and in the body are bacteria and other microbes.
What Are Normal Flora Microbes?
Normal flora bacteria cover our skin, mucous membranes and colonize our intestines.
Page last updated: 3/2016
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
 | ||||||
Many normal flora provide direct benefits, such as making vitamins or aiding digestion. Even if normal flora microbes merely take up space and resources, they help prevent pathogens (disease causing microbes) from easily invading the body and causing illness.
Although there are many different species of normal flora, these microbes typically fall into one of two categories: 1. resident microbes & 2. transient microbes.
Resident microbiota typically colonize the surface of the skin, mucous membranes, digestive tract, upper respiratory system and distal portion of the urogenital system. These microbes do not typically harm the host, while they benefit from feeding on the cellular waste and dead cells of the host's body.
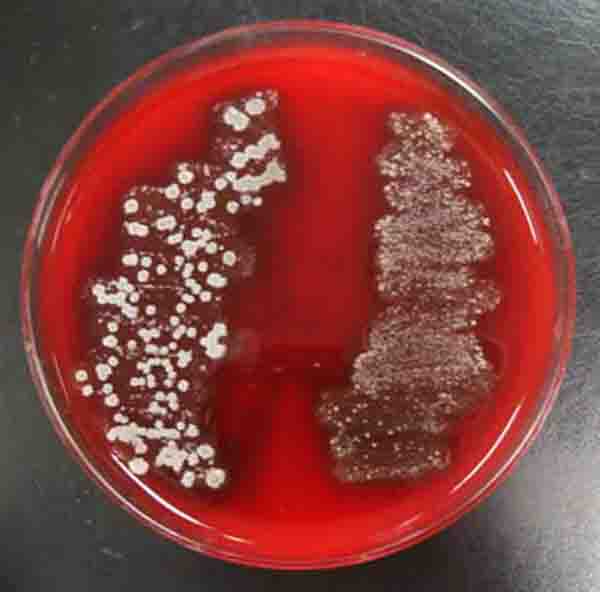
Arm plate of TSY agar that was used to take a normal flora sample from the skin. After incubation, plate now shows bacterial colonies of normal flora.
Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
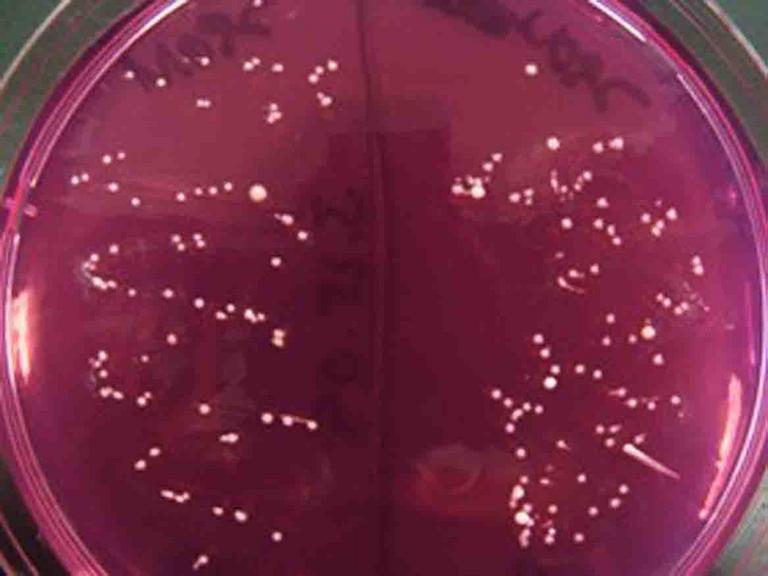
Tiny, white punctiform colonies of Staphylococcus epidermidis, resident
normal flora from inside the nose, growing on Mannitol Salt Agar.
Resident Microbiota
The body’s resident microbiota are just that — residents. These species are life-long members of the body's normal microbial community, but are not found everywhere. There are many areas of the human body that remain axenic, and, in the absence of disease, are never colonized by normal flora. Sterile areas include the body cavity, lungs, central nervous system, circulatory system and upper urogenital regions.