| ||||
What Are Normal Flora Microbes? - P2
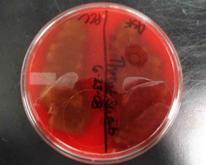
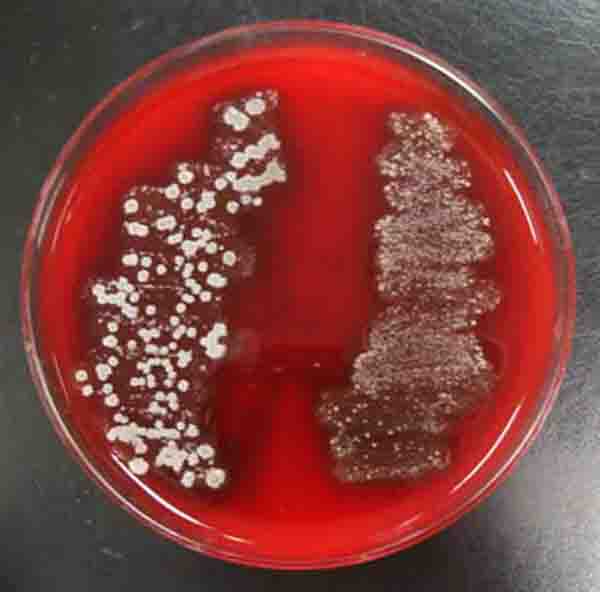
Blood agar (BAP) inoculated with two throat swab samples. Top photo: Bacterial colonies growing on the surface of BAP. Bottom photo: When place is viewed from bottom, agar appears bruised. This is called alpha hemolysis, and indicates normal flora.
Page last updated: 3/2016
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
PAGE 2 < Back to Page 1
Opportunistic Pathogens
Under normal conditions, resident and transient microbes cause the host no harm. However, if the opportunity arises, some of these microbes are able to cause disease and become opportunistic pathogens. This can happen due to a number of different conditions:
- When the immune system isn’t working properly, normal flora can overpopulate or move into areas of the body where they do not normally occur.
- When the balance of normal microbes is disrupted, for example when a person takes broad spectrum antibiotics, microbes that are normally crowded out by resident microbes have an opportunity to take over. Tougher, antibiotic resistant bacteria, or yeast can get the upper hand.
Transient Microbiota
Transient microbes are just passing through. Although they may attempt to colonize the same areas of the body as do resident microbiota, transients are unable to remain in the body for extended periods of time due to:
- difficulty competing with established resident microbes
- elimination by the body’s immune system
- physical or chemical changes within the body that discourage the growth of transient microbes
- Disease can result when normal flora are introduced to an area of the body that is normally axenic, or a location that they do not normally occur in. Bladder infections, typically caused by normal flora E. coli from the colon, are an example of this. Invasive medical procedures that introduce catheters or surgical wounds can also allow microbes into areas of the body that are normally sterile.
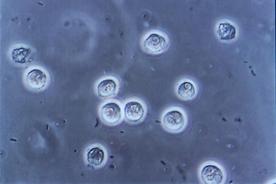
Multiple bacilli (rod-shaped bacteria, here shown as black and bean-shaped) between round white blood cells in urinary microscopy, indicative of urinary tract infection.
Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources.