| ||||
Acid-fast Ziehl Neelsen Stain Reaction
Differential Test to Identify
Mycobacterium & Nocardia Bacteria
Many bacteria of the genera
Mycobacterium and
Nocardia are medically significant, causing infectious diseases such as tuberculosis, leprosy and other lung and skin infections.
Article Summary: Acid-fast staining is used to identify bacteria of the genera Mycobacteria & Nocardia, which have mycolic acid in their cell wall. Here's how it works.
Acid-fast Ziehl-Neelsen Stain Reaction
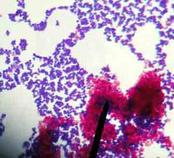
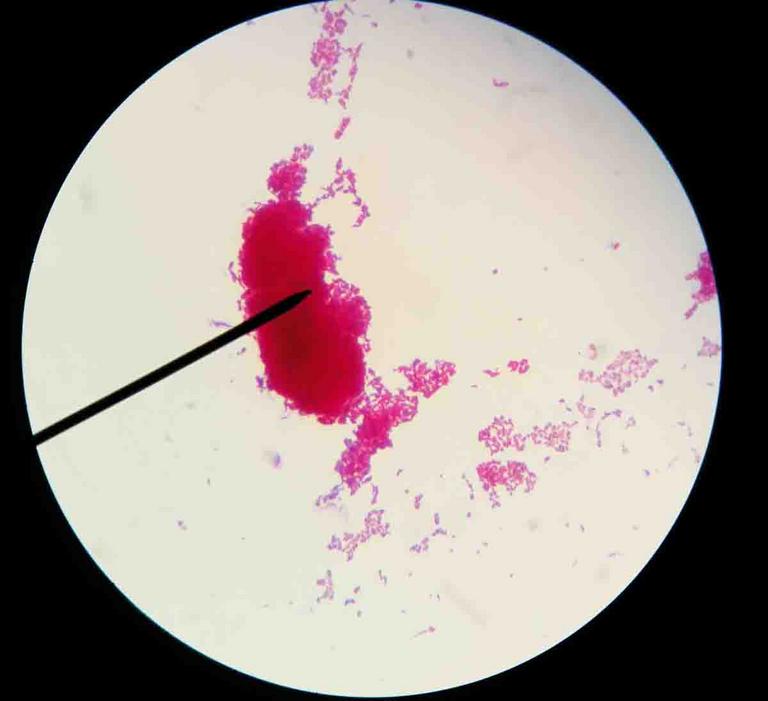
Acid-fast bacteria
Mycobacterium smegmatis
viewed under oil immersion @ 1000xTM
SPO Video: How to Prepare a
Bacterial Smear for
Acid Fast (Ziehl-Neelsen) Stain
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
 | ||||||
Page last updated:
8/2015
Therefore, it is clinically important to be able to accurately identify members of these genera. The acid-fast stain is a first step in identification of these types of bacteria.
Cell Wall of Mycobacteria and Nocardia
The Gram stain is a differential stain reaction that is used to categorize most bacteria as either Gram+ or Gram-. This distinction is due to differences in the bacterial cell wall structure of these two categories of bacteria and has significance with respect to which antibiotics can be used to kill or control bacteria.
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in two college-level introductory microbiology courses (8-week & 16-week). The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
Because the cell wall is resistant to water-based stains, acid-fast organisms require a special staining technique involving heat to drive stain into their waxy cell wall.
Bacteria of the genera Mycobacterium
and Nocardia have unusual cell walls that are waxy and nearly impermeable due to the presence of the molecule mycolic acid. Bacteria that produce mycolic acid are highly resistant to disinfectants, desiccation and are difficult to stain with water-based stains such as the Gram.
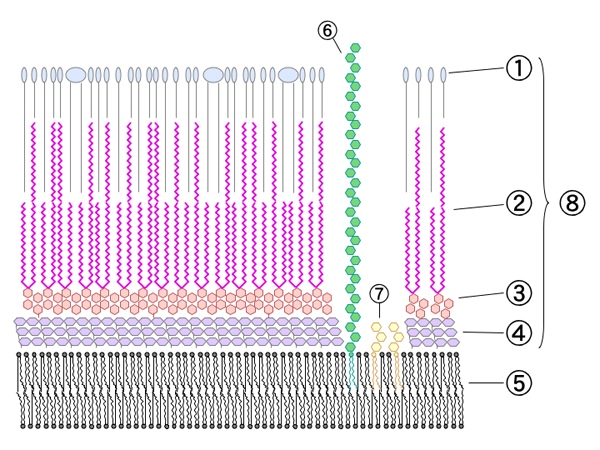
Diagram of Mycobacterial cell wall:
1.outer lipids; 2.mycolic acid;
3. polysaccharides; 4. peptidoglycan;
5. plasma membrane; 6. lipoarabinomannan (LAM); 7. phosphatidylinositol mannoside;
8. cell wall skeleton
Heat Fixing a Bacteria Smear
Prior to staining bacteria, a bacterial smear must be heat fixed onto a microscope slide. A smear is a sample of bacteria suspended in a small amount of water on a slide. That sample is then dried using heat.
The heat kills the bacteria and attaches the sample to the slide so that it does not easily wash away.