| ||||
Acid-fast Ziehl-Neelsen Staining of Bacteria - P3
Acid-fast Stain Reaction Explained
Primary stain: The hot pink appearance of Acid-fast cells is caused by Carbol fuchsin, the primary (first) stain, which is driven into acid-fast cells using the heat from a water bath.
Decolorizer: This step does not remove the Carbol fuchsin stain trapped within the waxy, acid-fast cell wall, but does remove the stain from bacterial cells that do not have wax in their cell wall.
Application of Primary Stain: 1. Carbol fuchsin primary stain of acid-fat stain; 2. Carbol fuchsin being applied to slide that had been prepared with acid-fast controls and an unknown bacteria. Blotting paper has been put on top of the slide. Then the blotting paper is saturated with stain and heated over water bath; 3. Clothes pins are useful for handling the slide; 4. Blotting paper is discarded and slide is rinsed.
Application of Decolorizer: 1. Acid alcohol decolorizer for acid-fast stain; 2. Drizzle decolorizer down slide for 10 - 15 seconds, while watching to see that stain is removed from negative control; 3. Rinse.
Application of Counterstain: 1. Secondary stain (counterstain), crystal violet; 2. Crystal violet is applied to slide and left for one minute; 3. Rinse; 4. Stained acid fast slide, with + control on left, unknown in center and - control on right. Go to > More acid-fast stain photos.
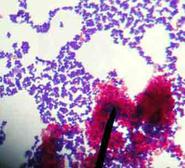
Hot pink acid-fast bacteria Mycobacterium smegmatis, and nonacid-fast bacteria (dark purple) viewed under oil immersion
@ 1000xTM
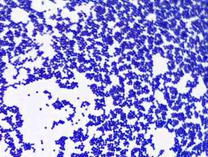
Non-acid-fast bacteria Staphylococcus epidermidis viewed under oil immersion @ 1000xTM
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
Page last updated: 8/2015
Photographic Guide to the Acid-fast Stain
Double click on photo strip for a slideshow of larger images.
SCIENCE VIDEOS
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in two college-level introductory microbiology courses (8-week & 16-week). The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
Sources and Resources
- Schauer, Cynthia (2007) Lab Manual to Microbiology for the Health Sciences, Kalamazoo Valley Community College.
- Identification of Unknown Bacteria Lab Exercise Main Page from the Virtual Microbiology Classroom
- How to Use a Compound Light Microscope, SPO Class Note Article
- Viewing Bacteria Using Oil Immersion Technique, SPO Class Notes Article
- Bauman, R. (2014) Microbiology with Diseases by Taxonomy 4th ed., Pearson Benjamin Cummings..
PAGE 3 < Back to Page 2
Secondary stain (counterstain): The crystal violet counterstain imparts purple color to the colorless nonacid-fast bacteria, but doesn't change the color of acid-fast cells.
After this staining procedure, the Acid-fast cells will appear pink because the primary stain, Ziel’s carbol fuschion, has been driven into the bacteria’s waxy cell wall with the heat from the water bath. Acid-fast cells also typically clump together, due to the wax in their cell wall.
The nonacid-fast cells (bacteria that do not have a waxy cell wall) will appear purple, having retained the counterstain, crystal violet, after the primary stain was removed by the decolorizer.
 | ||||||
SPO is a FREE science education website. Donations are key in helping us provide this resource with fewer ads.
Please help!
(This donation link uses PayPal on a secure connection.)