| ||||
Diffusion, Osmosis and Tonicity:
How Osmotic Pressure Impacts Biological Cells
What Is Diffusion?
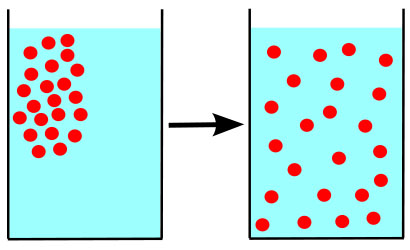
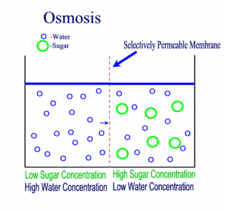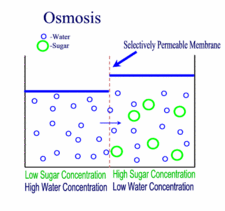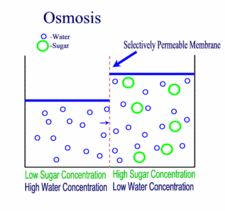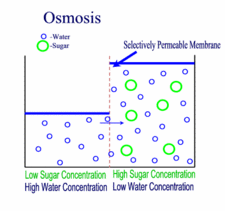
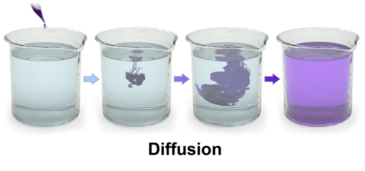
Diffusion is the passive transport of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration; and, surprisingly, you are very familiar with this process, whether you realize it or not.
Article Summary: Looking for a simple explanation of the potentially confusing terms 'diffusion', 'osmosis' and 'tonicity'? Here you go.
Diffusion, Osmosis & Tonicity
Page last updated: 3/2016
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
 | ||||||
When you put on perfume or aftershave, you can't just do it once and stay smelling sweet for the rest of your life (much to the relief of perfumers).
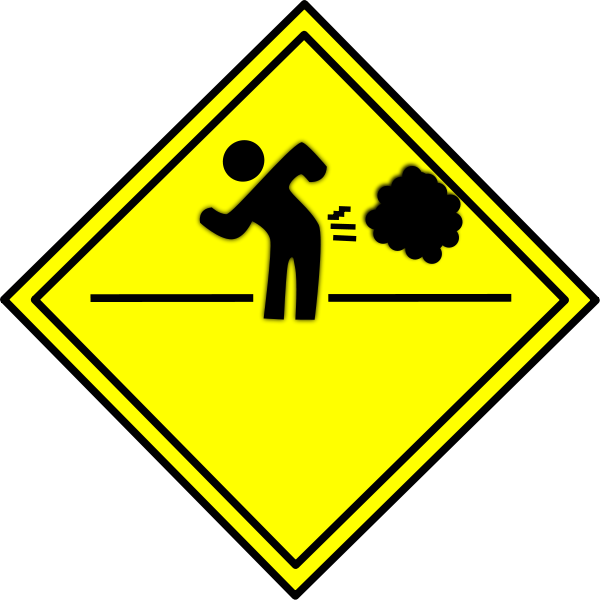
Another unpleasant example of diffusion is the very recognizable smell of skunk stink. If you are driving down the road towards a dead (or detonated) skunk, the unpleasant smell gets stronger and stronger as your car approaches the skunk, and weaker as you move away.
This is because the stinky molecules are more concentrated closer to their skunky source.
Video from Crash Course Chemistry
Passing Gases:
Effusion, Diffusion and the Velocity of a Gas
The molecules of scent slowly diffuse from the area where you applied them, until so many have departed that you can no longer detect your signature scent.
That's why farts aren't forever. When you let one fly, the fart molecules eventually spread out so much that the scent of your "bottom burp" is no longer detectable. Fanning the air behind your bum helps this happen faster.
 | ||||
Science Prof Online
has several
Virtual Classrooms
including:
(15 week)
(15 week)
(8 week)
(8 week)
(15 week)