| ||||
Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells - P2
Features of Eukaryotes
Eu = “true”,
karyon = “nucleus”
Eukaryotic cells are larger, more complex and more evolutionarily recent than prokaryotes. Whereas prokaryotes are bacteria and Archaea, eukaryotes are literally everything else ... amoebae, earthworms, mushrooms, grass,
bugs, you.
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in a college-level introductory Cell Biology Course. The Virtual Cell Biology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including Power Point Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
Page last updated: 3/2016
PAGE 2 < Back to Page 1
End of Article
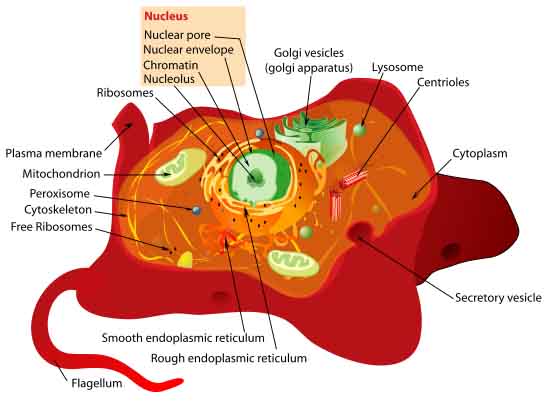
Endomembrane system of eukaryotic cell, showing nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus & plasma membrane. Click here for a labeled diagram.
The most noticeable feature that differentiates these more complex cells from prokaryotes is the presence of a nucleus; a double membrane-bound control center separating the genetic material, DNA (deoxyribo-nucleic acid), from the rest of the cell.
Eukaryotic cells also have an endomembrane system composed of different membrane-bound organelles that transport materials around the cell. The endomembrane system includes the nuclear membrane, rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus and different types of transport vesicles.
These vital organelles are involved in metabolism and energy conversion within the cell.
Depending on the organism, eukaryotic cells can reproduce in one of several ways, including meiosis (sexual reproduction) and mitosis (cell division producing identical daughter cells).
Illustration of a generic eukaryotic animal cell. Click here for a practice assignment on identifying the parts of an animal cell.
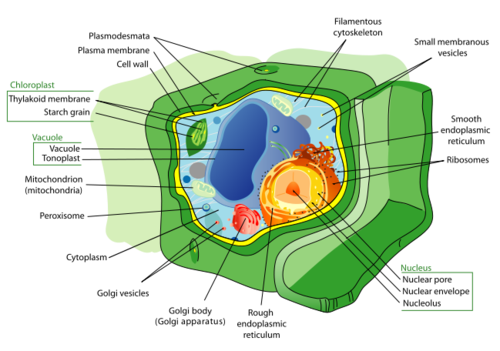
Illustration of a generic eukaryotic plant cell.
We have loads of information and illustrations on eukaryotic cell structure and function. Please select from the topics below to find what you need:
Sources & More Resources on Biological Cells
- Bauman, R. (2014) Microbiology with Diseases by Taxonomy, Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
- Park Talaro, K. (2008) Foundations in Microbiology.
- Inside a Cell, interactive cell diagram from University of Utah.
- Eukaryotic Cell Tour interactive exercise.
- Tour of a Cell Video by Paul Anderson.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum & Golgi Apparatus interactive lesson.
- Cell Structure Interactive Animation from Wiley.com
FREE Educational Materials on Cell Structure
- Prokaryotic Cell Structure & Function Lecture Main Page from the VCBC.
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in two college-level introductory microbiology courses (8-week & 16-week). The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
SPO VIDEO: How to Make a Wet Mount of Stained Epithelial Cheek Cells
 | ||||||