| ||||
Moon Cactus
Gymnocalycium mihanovichii friedrichii
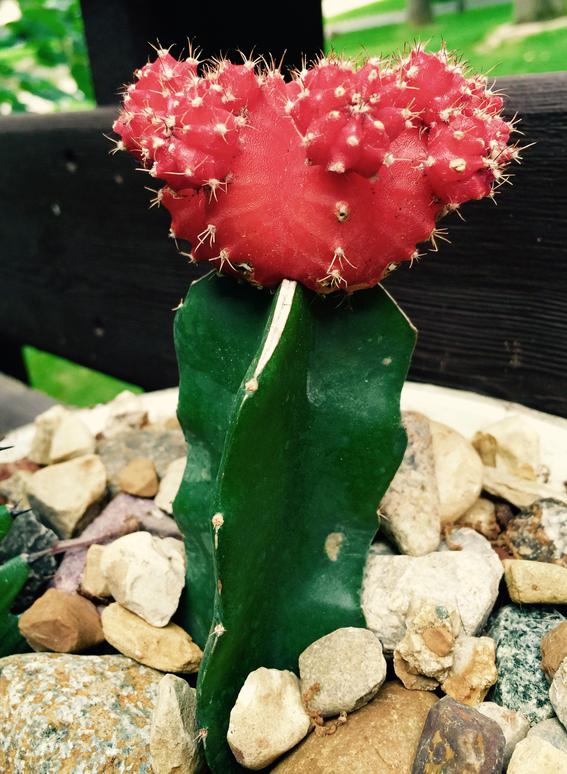
The Bottom of the Coral Cactus
The green base of this beautiful "Franken-cactus" is usually Hylocereus, a genus of about 20 different types of cacti that produce large, white, night-blooming flowers and edible fruit, also known as dragon fruit or strawberry pears.
Hylocereus has triangular-shaped stems with few spines. In their natural, South American environment,
they are climbers, with stems that can grow up to 30 feet, and horizontal roots that can attach to surrounding objects.
Article Summary: Gymnocalycium mihanovichii, commonly called Moon Cactus, is actually two plants that have been grafted together. Here's how to care for this short-lived, unusual beauty.
A Moon Cactus Is Two Plants in One!
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
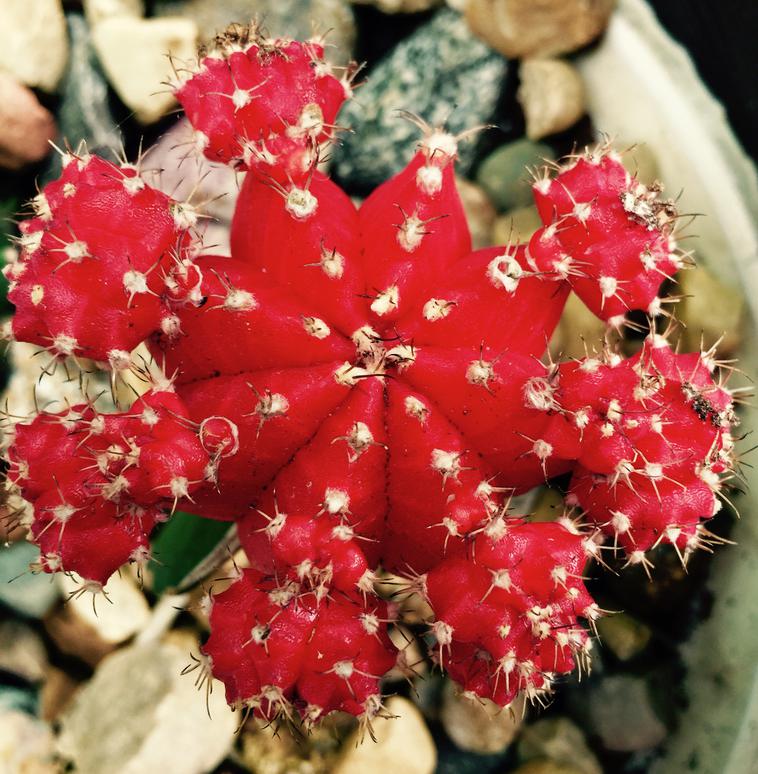
The Top of The Moon Cactus
The showy part of the plant, the "moon" (also known at the scion), is a mutant of the cactus species
Gymnocalycium mihanovichii.
 | ||||||
Above: Hylocereus monacanthus cactus in bloom. Below: Red pitaya (Hylocereus undatus) fruit, also known as dragonfruit.
Continued ...
Page last updated: 6/2015
The graft usually only lasts a few years, because the
Hylocereus base grows faster than the Gymnocalycium scion.
Normal and mutant
Gymnocalycium
produce offsets that look like budding little baby cacti. These offsets can be cut off and then grafted onto bases. That is how more moon cacti are produced.
Why Can't Mutant Moons Make Food?
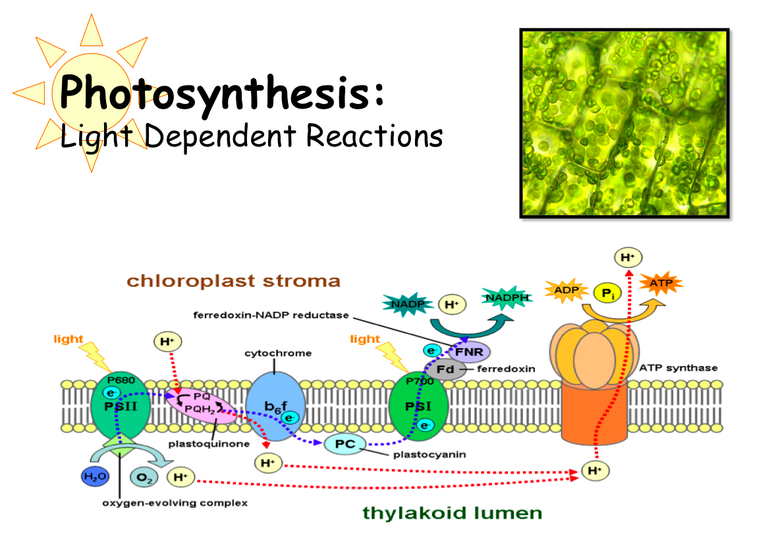
Get your nerd on! Take a look at our biology lecture on photosynthesis, how plants make food out of sunlight.
The difference in the speed of their growth eventually becomes too great for the graft to hold, and the two parts separate. The parts can be regrafted. See Page 3 for information on Grafting Moon Cacti.
These mutants lack the pigment chlorophyll necessary for photosynthesis (how the plant makes food from sunlight energy), and cannot survive unless grafted onto a plant that has chlorophyll. Without the green pigment the other colors of the cactus show through, and the moons are typically yellow, orange or red.
A normal, green-pigmented
Gymnocalycium mihanovichii.